Paediatric Sickle Cell Anaemia
Overview
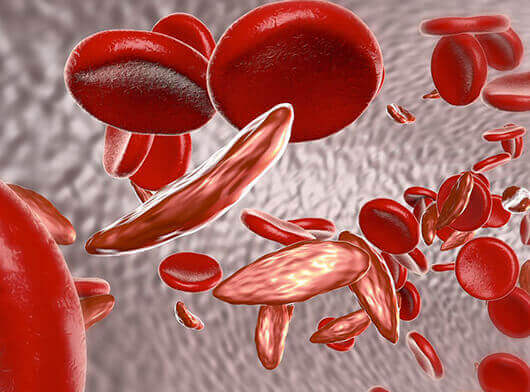
Sickle cell anemia is an inherited red blood cell disorder in which there is not enough healthy red blood cells (RBCs) to carry oxygen through the body. The RBCs are normally round which move easily through blood vessels.
Risk Factors
A family history of Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) increases a child’s risk for the disease. In addition, one or both parents carrying the mutated gene (carriers) increases a child’s risk for the disease.
Signs and Symptoms
Each person may experience symptoms differently. Some of the symptoms are:
- Hand-foot syndrome – Painful swelling of the fingers..
- Read More
Diagnosis
Blood test - Complete blood count (CBC) including Hemoglobin (Hb) to rule out sickle cell anemia. Other tests include Haematocrit count, Reticulocyte count, Hb electrophoresis, Urine analysis, Serum bilirubin,..
Treatment
Hydration and Medications - Drinking 8- 10 glasses of water is recommended. In some cases, IV (intravenous) fluids may be needed. Medications may be recommended depending on symptoms exhibited.
FAQ
- How does Sickle cell Anemia start?
- Can Sickle cell Anemia be cured?
- What lifestyle changes help reduce your risk of Sickle cell crisis
- Read More
