The three main types of treatment for these cancers are surgery, radiation and chemotherapy. Most of these cancers will need surgery and /or radiotherapy. Chemotherapy is usually given when cancer has spread too far to be treated with surgery and radiotherapy. It is also given before or along with radiation with the goal of preserving the voice box.
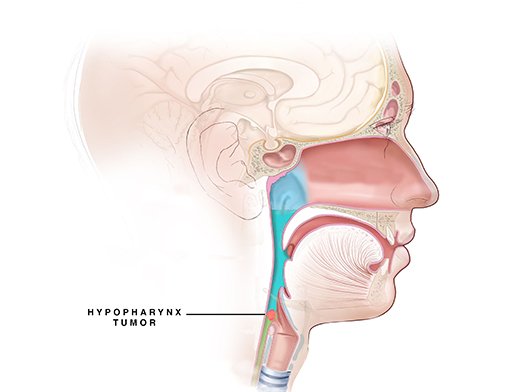
Hypopharyngeal Cancer
Treatment

.png)

- Surgery
- Radiation Therapy
- Medical Management
- Surgery is considered depending on the tumor’s size, location and the overall health of the patient. Some people need more than one surgery.
- Surgery may be:
- Tumor resection - The surgeon will remove as much of a tumor as possible as well as other tissues where cancer may have spread, such as lymph nodes or neck structures.
- Pharyngectomy - The surgeon removes part or all of the pharynx.
- Laryngopharyngectomy -The surgeon removes part or all of the pharynx and the larynx.
- Transoral CO2 laser resection -This approach involves specialized transoral endoscopes with an operating microscope coupled to a CO2 laser.
- Trans-oral robotic surgery - In selective patients, robot-assisted minimally invasive surgery is performed. These minimally invasive procedures allow the surgeon to perform the surgery through small incisions. This reduces hospital stay and speeds up recovery.
- Surgery may affect how you eat, breathe or talk and hence reconstruction of the removed section might be necessary.
-
Reconstructive surgery - In advanced cases, surgeons sometimes rebuild structures (such as the pharynx or create a voice prosthesis) during the same or a second procedure. Reconstructive surgery is done using the microvascular technique.
During a total laryngopharyngectomy, the continuity between the pharynx and esophagus is lost. This is reconstructed using a small portion of the Jejunum (small intestine) using microvascular techniques.
In cases where the tumor extends into the esophagus the stomach is brought to the neck region and connected to the pharynx, and when the voice box is removed, a voice prosthesis is placed. - Speech or swallowing therapy - Post-surgery, the doctor may recommend rehabilitation to improve the function of speech and swallowing.
-
Since surgical treatment for Hypopharyngeal cancer involves the removal of the voice box, radiotherapy is the treatment of choice for small tumors. Radiotherapy is most commonly used after surgery to kill cancer cells that are not visible during surgery.
In some cases, when the tumor is extensive, and cure is not possible, radiation is given to ease for easing symptoms like pain, bleeding and swallowing. - Early-stage tumors can be treated with 3D conformal radiotherapy (3D CRT).
- Locally advanced tumors are better treated with high precision irradiation techniques like IMRT (intensity modulated radiotherapy), IGRT (image guided radiotherapy), and Rapid Arc or Proton beam therapy. High precision irradiation techniques can reduce side effects like xerostomia (dryness in the mouth), and difficulty in swallowing and result in a better quality of life.
- Chemotherapy
- Chemotherapy uses drugs to destroy cancer cells. The indication for chemotherapy is based on the stage of cancer and risk factors.
- Chemotherapy may be used before surgery to shrink large tumors, which makes it easier for the removal of the tumor.
- Few patients may require chemotherapy after surgery which helps to kill any residual cancer cells. It is also indicated in cases when the disease has spread to other parts of the body.
- Chemotherapy also may be used in cancers where the tumor is inoperable. Sometimes chemotherapy is combined with radiation therapy.
- Targeted drug therapy- The indication for targeted therapy is based on molecular changes in the cancer cell. This is usually combined with chemotherapy and may be an option in selected cases. In the case of recurrent disease, based on the molecular alterations noted in the tumor, specific targeted therapy is also an option. These are given in combination with chemotherapy.
- Immunotherapy Immunotherapy is a drug treatment that uses the immune system to fight cancer. The indication for immunotherapy is based on immune-histochemical tests and molecular tests in advanced disease and recurrence. Generally, the patient tolerates immunotherapy well.
