- The lymphatic system is a part of our immune system. Clear fluid called lymph flows through the lymphatic vessels and contains infection-fighting white blood cells, known as lymphocytes.
- The main types of lymphocytes are T-cells and B-cells, which are white blood cells made in the bone marrow. B-cells remain in the bone marrow to mature, while T-cells mature in the thymus, a small organ nestled between the lungs.
- Lymphoma begins when healthy cells in the lymphatic system change and grow out of control. This uncontrolled growth may form a tumour, involve many parts of the lymphatic system, or spread to other parts of the body. B-cells are far more likely than T-cells to mutate and cause cancer such as Hodgkin lymphoma, non-Hodgkin lymphoma or leukaemia.
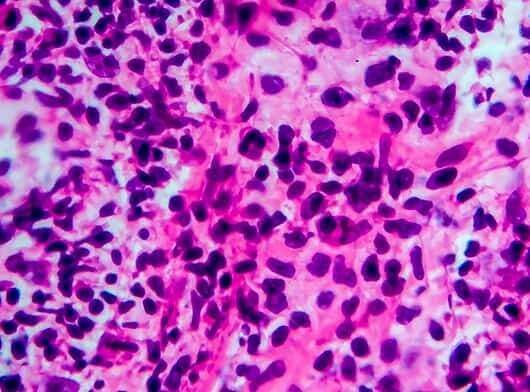
- The main difference between Hodgkin lymphoma and Non-Hodgkin lymphoma is the presence or absence of oversized B-cells called Reed-Sternberg cells. These cells are usually detected during a biopsy and indicate the presence of Hodgkin lymphoma.
Hodgkin's Lymphoma
LYMPHOMA

.png)

HODGKIN’S LYMPHOMA
- Hodgkin's lymphoma — formerly known as Hodgkin's disease — is a cancer of the lymphatic system, which is a part of our immune system. It may affect people of any age, but is most common in people between 20 and 40 years old and those over 55.
Hodgkin lymphoma types
- Nodular sclerosis: This is the most common subtype of classical Hodgkin lymphoma. It often occurs in children and young adults, especially young women, and is most often found in the chest and/or neck. This subtype may cause fibrous scars in the lymph nodes.
- Mixed cellularity: This accounts for about 25 percent of all classical Hodgkin lymphoma cases and is more common among older adults. This subtype is often found in the abdomen.
- Lymphocyte-rich: This form of Hodgkin lymphoma accounts for 5 percent of all classical cases and is most often diagnosed in men.
- Lymphocyte-depleted: This extremely rare disease represents less than 1 percent of all Hodgkin lymphomas and is most often diagnosed in older adults or people with HIV.
- A less common type is nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphoma (NLPHL), which affects about 5 percent of Hodgkin lymphoma patients. NLPHL is characterized by the presence of so-called popcorn cells, lobular versions of Reed-Sternberg cells that resemble popcorn. NLPHL is most often diagnosed in middle-aged adults
