- Procedures
- Imaging
- Laboratory
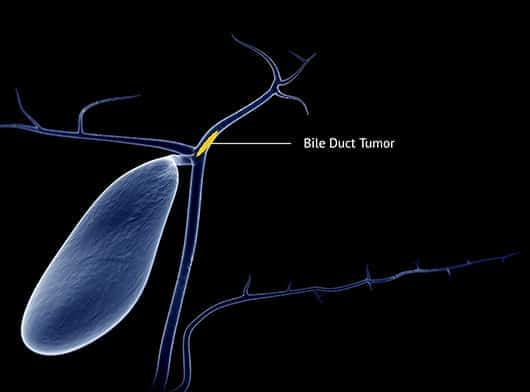
- Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) - It is a nonsurgical procedure to examine, diagnose and treat problems in the liver, gallbladder, bile ducts, and pancreas using an endoscope. During an ERCP, a thin tube equipped with a tiny camera is passed down through the throat to the small intestine. It is used to examine the junction of the bile ducts connecting to the small intestine. This procedure is also used to inject a dye for further imaging.
- Biopsy - A sample of tissue is removed from the suspicious lesion and sent to the lab for further pathological evaluation.
- CT scan is a diagnostic imaging procedure that uses x-rays to build cross-sectional images of the body. It also helps to identify the spread of cancer.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) uses the interaction of radio waves and magnetic field which is processed in a high-speed computer system to produce detailed scan pictures of the tissue, organs, bones, ligament and cartilage. It may be useful in detecting tumors and their metastases. This diagnostic technique offers greater soft tissue contrast than a CT scan.
- PET CT is considered to assess spread to regional nodes or distant metastases to other parts of the body. It provides functional and morphological details by utilizing radiation derived from Isotope labeled Glucose molecules to detect cellular glucose uptake, in cancer.
- Blood Tests
- Liver Function test - A sample of blood is collected and tested for the levels of bilirubin, liver enzyme and alkaline phosphatase which is released into the blood by the liver. Elevated levels of these substances may be suggestive of liver disease.
- Tumor Markers - Elevated levels of cancer antigen (CA) 19-9 in the blood may be suggestive of bile duct disease (such as bile duct inflammation and obstruction).


.png)
